- Only single output neuron fires
- Set of homogeneous neurons with some randomly distributed synaptic weights
- Respond differently to given set of input patterns
- Limit imposed on strength of each neuron
- Mechanism to allow neurons to compete for right to respond to a given subset of inputs
- Only one output neuron active at a time
- Or only one neuron per group
- Winner-takes-all neuron
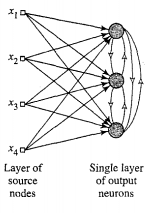
- Lateral inhibition
- Neurons inhibit other neurons
- Winning neuron must have highest induced local field for given input pattern
- Winning neuron is squashed to 1
- Others are clamped to 0
- Neuron has fixed amount of weight spread amongst input synapses
- Sums to 1
- Learn by shifting weights from inactive to active input nodes
- Each input node relinquishes some proportion of weight
- Distributed amongst active nodes
- Individual neurons learn to specialise on ensembles of similar patterns
- Feature detectors
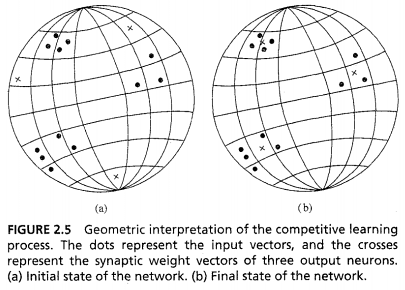
- Feature detectors