Pattern Association
- Associative memory
- Learns by association
- Autoassociation
- Store a set of patterns by repeatedly presenting them in the network
- Then presented partial or distorted stored pattern
- Recall intended
- Input and output data spaces are same dimensionality
- Store a set of patterns by repeatedly presenting them in the network
- Heteroassociation
- Arbitrary set of input patterns paired with another arbitrary set of output patterns
- Supervised instead of unsupervised
- No required relationship between input/output dimensionality
- Arbitrary set of input patterns paired with another arbitrary set of output patterns
- Stages
- Storage
- Recall
Pattern Recognition
- Received pattern/signal is assigned to one of a prescribed number of classes
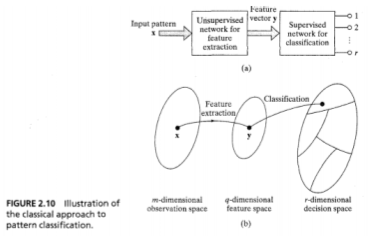
Function Approximation
- System Identification
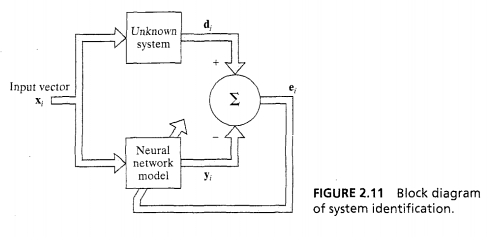
- Inverse System
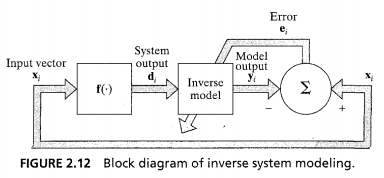
Control
- Learn to control a process or critical part of a system
Filtering
- Filtering
- Extraction of information about a quantity of interest at discrete time by using data from time up to
- Smoothing
- Use information past time
- Expect smoother result
- Delay in processing
- Use information past time
- Prediction
- Predict later data using current and previous
Beamforming
- Spatial filtering
- Distinguish spatial properties of a target signal and background noise
- Similar to bats
- Used in radar and sonar