Networking
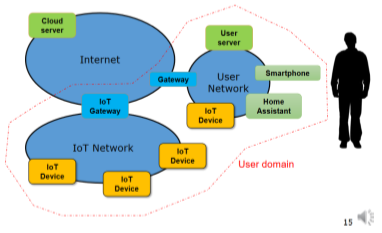
Gateway
- Connects IoT devices to internet
- Operator deployed
- LTE etc
- Self-deployed
- Wi-Fi
Roles
- Machine-to-machine connections
- Cheaper telecoms cost
- Cheaper hardware
- Not everything has to be LTE connected
- Simpler config
- Translate protocols between IoT and internet
- Processing data
- Encrypting, filtering, consolidating
- Boundary between networks
- Security
Network Module
- 802.15.4 only a channel
- End-to-end provided by network module
- Multi-hop wireless network
- Wireless sensor networks (WSN)
- Wireless mobile ad hoc networks (MANET)
- Wireless mesh network (WMN)
- Vehicular ad hoc network (VANET)
Roles
- Management
- Packet
- Adapting size and format
- Address
- Adapting and/or resolving addresses
- Device
- Joining/leaving of nodes
- Service
- Add-ons such as security
- Packet
- Operational
- Route discovery & maintenance
- Packet forwarding
Performance
- Power consumption
- Limited supply
- Significant power in communications
- Network Lifetime
- Duration of proper operation
- Before no longer provides services
- When a node fails
- Design-time
- Design deployment that will last
- Run-time
- Dynamic operation to conserve energy usage
- All layers
- App
- Consolidating data
- Adaptive frequency for data grouping
- Network
- Avoid aggressive topology maintenance
- MAC
- Duty-cycle MAC to keep radio asleep
- Physical
- Power level control
- App
Issues
- Bottleneck
- One node relaying lots of data
- Bad placement of gateway
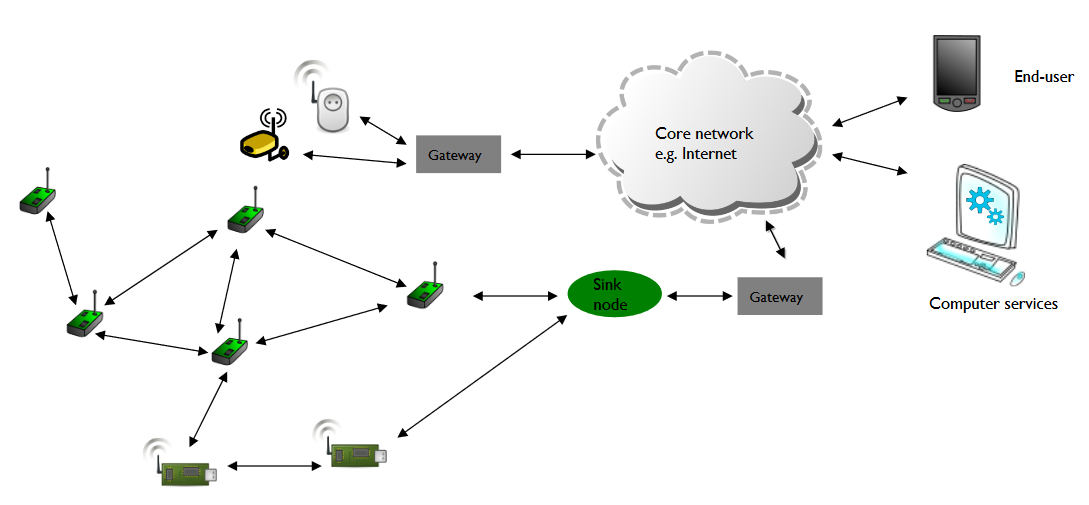
- Low power devices
- Multi-hop